I. The Prehistoric Era (c. 3.3 million years ago - c. 3000 BCE):
Paleolithic Era (Old Stone Age)
The emergence of Homo species in Africa. Development of basic stone tools, fire, and early forms of social organization. Hunter-gatherer lifestyles.

Mesolithic Era (Middle Stone Age)
A transitional period following the last Ice Age. Development of more sophisticated tools and adaptation to changing environments.

Neolithic Era (New Stone Age)
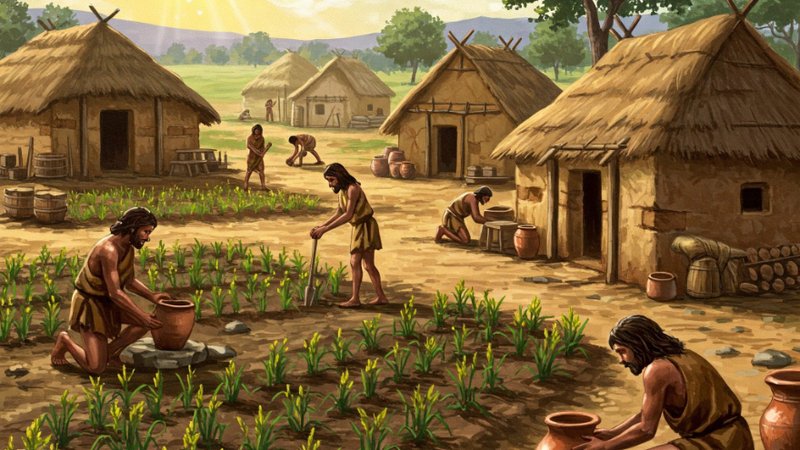
The Neolithic Revolution marks a fundamental shift with the development of agriculture and animal domestication. This led to settled lifestyles, the rise of villages, population growth, and the beginnings of social stratification and specialization of labor. The invention of pottery and weaving also occurred.

II. The Ancient World (c. 3000 BCE - c. 500 CE):
Rise of Civilizations
The development of complex societies with urban centers, organized government, specialized labor, social hierarchies, writing systems, and monumental architecture in Mesopotamia (Sumer, Akkad, Babylon, Assyria), Egypt, the Indus Valley, and China (Shang and Zhou Dynasties).

The Bronze Age
The discovery and use of bronze tools and weapons led to advancements in warfare, agriculture, and craftsmanship.

The Iron Age
The smelting of iron became widespread, leading to more durable tools and weapons, further impacting societies and warfare.

The Rise of Empires
Powerful states expanded their territories through conquest and political organization. Notable empires include the Akkadian Empire, the Egyptian New Kingdom, the Persian Empire, the Roman Empire, and the Han Dynasty in China.

Development of Philosophy and Religion
Major philosophical and religious systems emerged, including Greek philosophy (Socrates, Plato, Aristotle), early forms of Buddhism and Hinduism in India, Confucianism and Taoism in China, and the development of monotheistic religions like Judaism.

Greco-Roman Civilization
The rise and influence of ancient Greece with its democratic ideals, philosophy, art, and science, followed by the Roman Republic and Empire, which dominated the Mediterranean world, leaving a lasting legacy in law, language, engineering, and governance.

Decline of Ancient Empires
Internal strife, economic problems, overextension, and external invasions led to the decline and eventual fall of many ancient empires, including the Western Roman Empire.

III. The Post-Classical Era (c. 500 CE - c. 1500 CE):
The Rise of New Civilizations and Empires
The Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire) flourished. Islam emerged in Arabia and rapidly spread across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe and Asia, leading to the establishment of vast caliphates and a golden age of Islamic scholarship and culture. Powerful kingdoms and empires rose in Europe (e.g., the Frankish Empire, the Holy Roman Empire), India (e.g., the Gupta Empire, the Delhi Sultanate), China (Sui, Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming Dynasties), and the Americas (Maya, Aztec, Inca).

The Middle Ages in Europe
A period characterized by feudalism, the dominance of the Catholic Church, the Crusades, and the gradual development of national monarchies.

The Mongol Empire
The unification of Mongol tribes under Genghis Khan led to the formation of the largest contiguous land empire in history, impacting trade and cultural exchange across Eurasia.

The Renaissance
A cultural and intellectual movement that began in Italy and spread across Europe, marked by a renewed interest in classical art, literature, and philosophy, and a spirit of humanism and inquiry.

Exploration and Trade
Increased trade networks connected different parts of the world, including the Silk Road, Indian Ocean trade, and trans-Saharan trade.
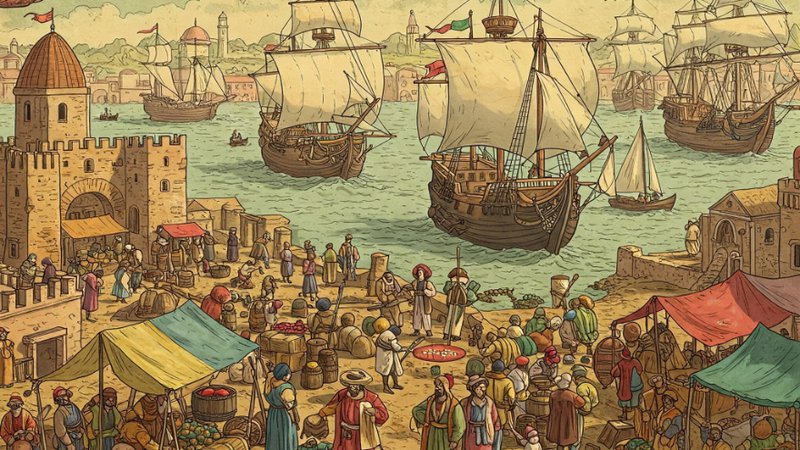

IV. The Early Modern Era (c. 1500 CE - c. 1800 CE):
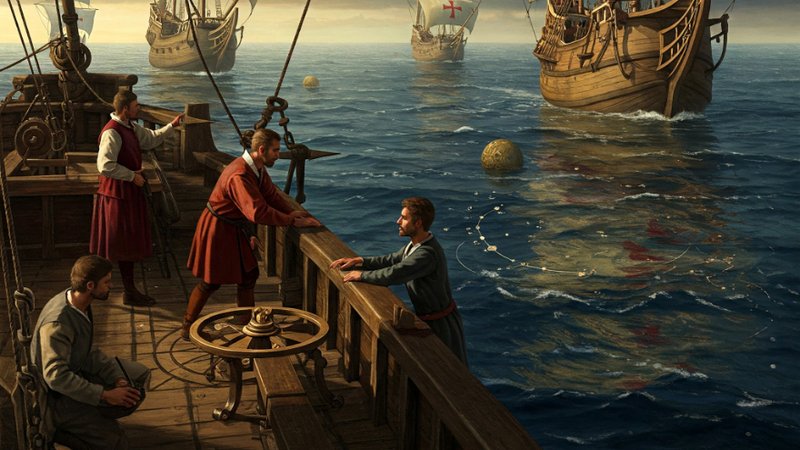
The Age of Exploration
European powers embarked on voyages of exploration, leading to the "discovery" of the Americas by Europeans, the establishment of global trade networks, and the rise of colonialism.

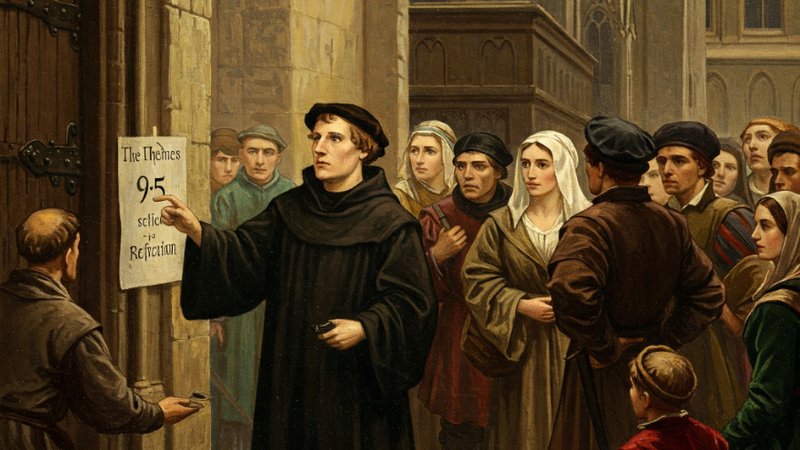
The Reformation
A religious movement that challenged the authority of the Catholic Church, leading to the rise of Protestantism and significant religious and political changes in Europe.

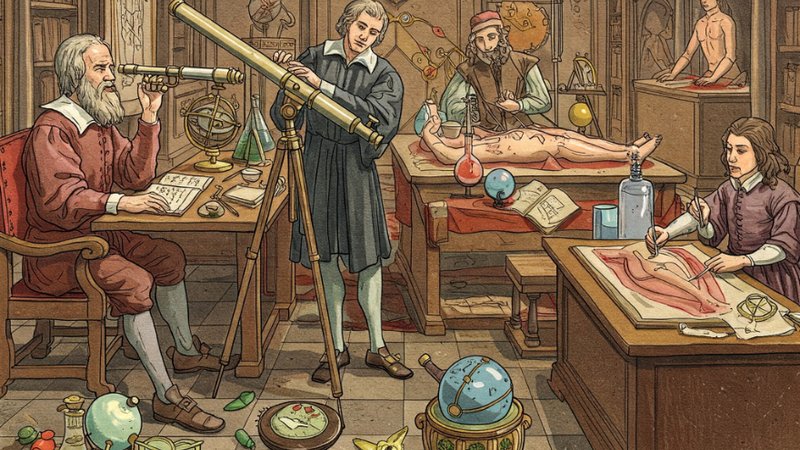
The Scientific Revolution
A period of major scientific advancements based on observation, experimentation, and reason, leading to new understandings of the universe and the development of new technologies.

The Enlightenment
An intellectual and cultural movement that emphasized reason, individualism, and human rights, influencing political thought and leading to revolutions.

The Rise of Nation-States
The consolidation of centralized monarchies and the development of national identities in Europe.
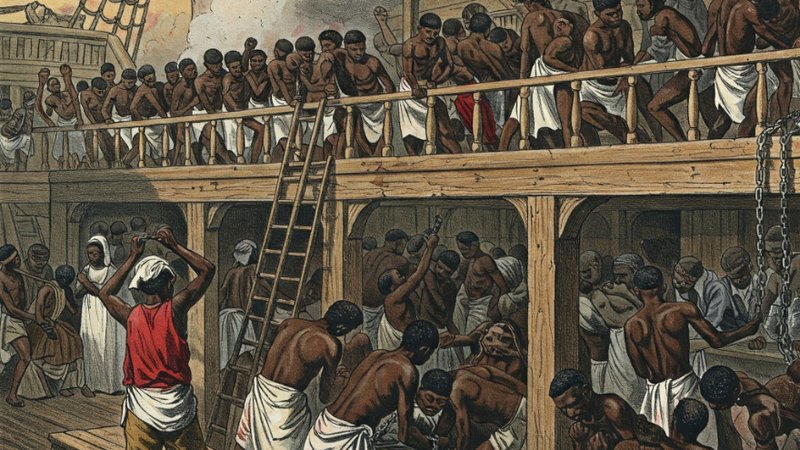
The Atlantic Slave Trade
The forced migration of millions of Africans to the Americas to work on plantations, a brutal and inhumane system with lasting social and economic consequences.

V. The Modern Era (c. 1800 CE - Present):
The Industrial Revolution
Beginning in Great Britain, this period saw unprecedented technological advancements, particularly in manufacturing, leading to urbanization, new social classes, and increased global interconnectedness.
Political Revolutions
The American Revolution and the French Revolution established new political ideals of democracy, liberty, and nationalism, inspiring movements for change around the world.
Imperialism and Colonialism
European powers and later other nations expanded their control over vast territories in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, exploiting resources and people, and shaping global power dynamics.
World War I (1914-1918)
A global conflict triggered by complex political and economic rivalries, leading to immense destruction and reshaping the political map of Europe.

The Interwar Period
A time of economic instability (the Great Depression), the rise of totalitarian ideologies (fascism, Nazism, communism), and increasing international tensions.
World War II (1939-1945)
The deadliest conflict in human history, resulting in the defeat of the Axis powers and the establishment of a new global order.

The Cold War (c. 1947-1991)
A period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, characterized by an arms race, ideological conflict, and proxy wars.
Decolonization
The dismantling of colonial empires and the emergence of independent nations in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean.
Globalization
Increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of nations through trade, communication, technology, and culture.
Technological Advancements
Rapid advancements in computing, communication, biotechnology, and other fields have profoundly transformed human society.
Contemporary Challenges
Issues such as climate change, inequality, terrorism, pandemics, and geopolitical instability continue to shape the world.
This summary provides a very broad overview. Each of these periods contains countless events, individuals, and developments that have shaped the world we live in today. Further exploration of specific regions and time periods will provide a much deeper understanding of the complexities of human history.

